Nukleotidy, also known as nucleotides, are tiny biological molecules, but their importance in the human body is enormous. Every living cell depends on them to function properly. They are the basic units that form DNA and RNA, which store and transfer genetic information. Without nukleotidy, life at the cellular level would not be possible. Beyond genetics, nukleotidy also play a key role in energy production through ATP, the main energy source for cells. From muscle movement and brain activity to immune defence and tissue repair, nukleotidy support almost every vital process.
This article explains nukleotidy in simple terms, covering their structure, types, biological functions, dietary sources, supplements, medical uses, and future potential in health and science.
Details Summary: Nukleotidy
| Field | Details |
|---|---|
| Term | Nukleotidy (Nucleotides) |
| Scientific Name | Organic molecules composed of a phosphate group, sugar, and nitrogenous base |
| Main Function | Building blocks of DNA and RNA; energy transfer via ATP |
| Found In | All living cells; present in food and dietary sources |
| Types | DNA nucleotides (A, T, G, C), RNA nucleotides (A, U, G, C), Energy (ATP, GTP) |
| Dietary Sources | Liver, fish, legumes, soy, mushrooms, whole grains |
| Medical Importance | Used in gene therapy, antiviral treatments, cancer research, immune support |
| Supplement Use | Recovery, gut health, infant nutrition, high-performance sports |
| Discovered In | Studied since the 19th century; foundational to molecular biology |
| Role in Wellness | Supports DNA repair, energy metabolism, immune system, and cell regeneration |
What Are Nukleotidy?
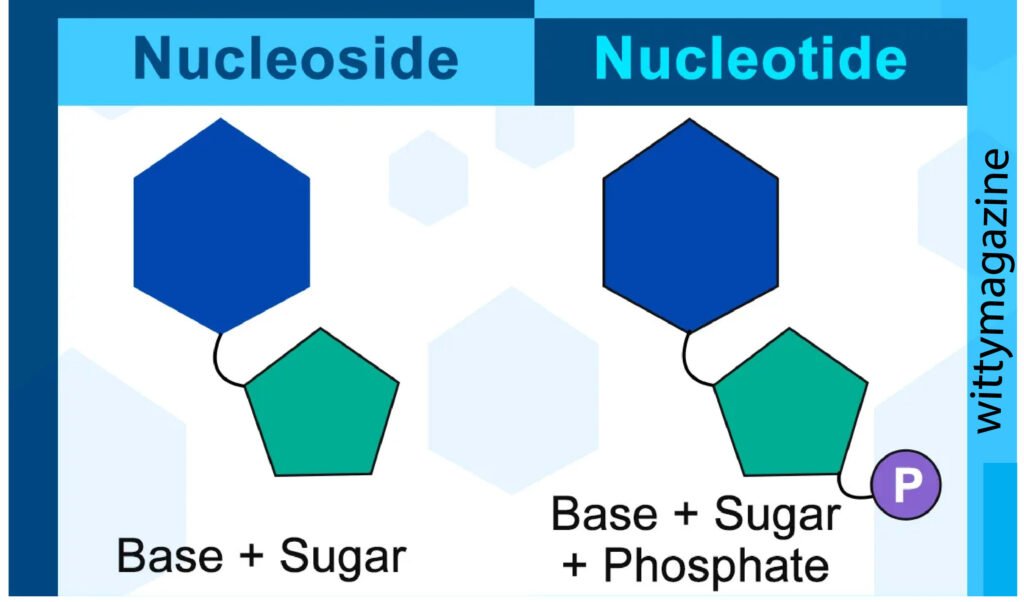
Nucleotides vs. Nukleotidy — Terminology
The word nukleotidy is simply another form of nucleotides, commonly used in scientific, medical, and nutritional contexts. Both terms describe the same biological compounds. You may see “nucleotides” in English research papers and “nukleotidy” in educational or international health content. The meaning remains the same. These molecules are essential in biology, genetics, nutrition, and medicine because they form the foundation of DNA, RNA, and cellular energy systems.
More From Info: Noelene Edwards: The Untold Life Behind Paul Hogan’s First Love
Basic Components of Nukleotidy
Each nukleotid is made of three basic parts:
-
Phosphate group – helps connect nucleotides together
-
Sugar molecule – ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA
-
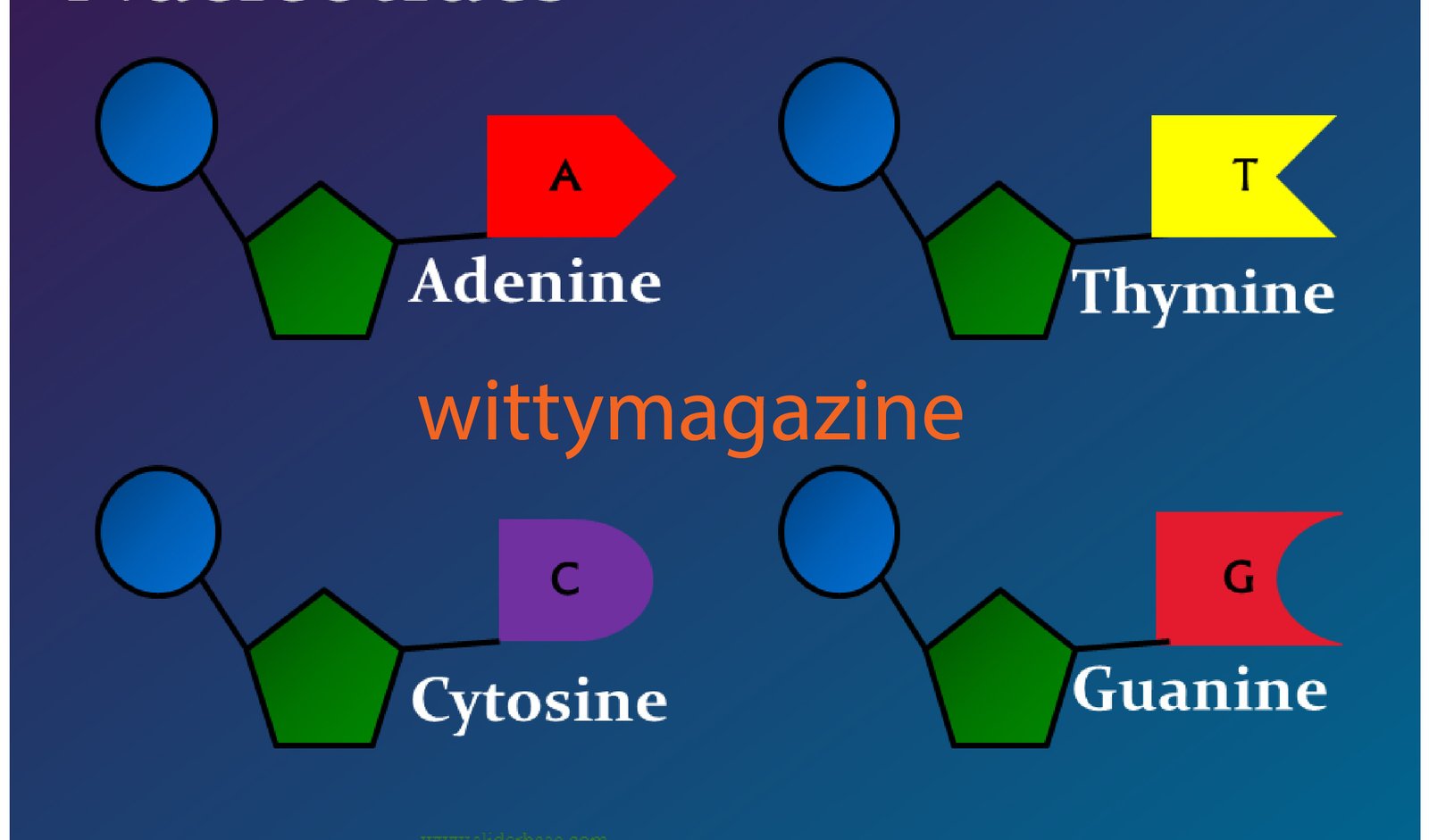
Nitrogenous base – adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), guanine (G), or uracil (U)
These three components combine to form a single nukleotid. When many nucleotides join together, they create DNA or RNA chains.
Structure of Nukleotidy — The Blueprint of Life
Key Elements and Their Role
Nukleotidy are divided into two main base groups:
-
Purines: adenine (A) and guanine (G)
-
Pyrimidines: cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U)
DNA uses A, T, C, and G, while RNA uses A, U, C, and G. The difference between DNA and RNA comes from both the sugar type and one nitrogen base. These small structural differences control how genetic information is stored and used.
How They Link: DNA/RNA Chain Formation
Nukleotidy connect through phosphodiester bonds, forming long chains.
In DNA, two chains twist together into a double helix structure.
In RNA, there is usually only one single strand.
These chains create the genetic code that controls growth, repair, reproduction, and inheritance. The sequence of nucleotides acts like letters in a biological language.
Types of Nukleotidy and Their Biological Roles
DNA Nucleotides
DNA nucleotides include adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine. Their specific order stores genetic instructions. These instructions determine physical traits, body functions, and how cells behave.
RNA Nucleotides
RNA uses adenine, uracil, guanine, and cytosine. RNA converts DNA instructions into action by helping make proteins.
Different types of RNA include:
-
mRNA – carries genetic messages
-
tRNA – delivers amino acids
-
rRNA – builds ribosomes
Energy-Related Nukleotidy
Some nucleotides store and transfer energy:
-
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) – main energy source
-
GTP, CTP, UTP – support cellular reactions
ATP powers muscle movement, brain activity, digestion, and metabolism.
Signaling Nukleotidy
Nukleotidy like cAMP and cGMP act as signaling messengers. They help cells communicate, respond to hormones, and regulate growth, metabolism, and immune reactions.
Functions of Nukleotidy in the Human Body
DNA/RNA Synthesis and Genetic Information
Nukleotidy store genetic information and allow DNA replication and repair. They ensure genetic material is passed correctly from one cell to another and from parents to children.
Cellular Energy Transfer
ATP, a nucleotide, is essential for energy transfer. Every cell uses ATP to perform tasks such as muscle contraction, nerve signaling, and chemical reactions.
Immune System Support
Nukleotidy support immune cell growth and repair. They help the body fight infections and recover faster from illness or injury by supporting tissue regeneration.
Cell Signaling and Growth
They regulate cell division, repair damaged cells, and control programmed cell death (apoptosis), which keeps tissues healthy.
Dietary Sources of Nukleotidy — What to Eat for DNA Health
Animal-Based Sources
Rich sources include:
-
Liver and organ meats
-
Fish and seafood
-
Poultry
-
Eggs and dairy products
Plant-Based Sources
Plant foods also provide nucleotides:
-
Lentils, beans, chickpeas
-
Soy products
-
Mushrooms
-
Whole grains
Bioavailability and Digestion
The body absorbs nucleotides from food and can also make them internally. Infants, athletes, elderly individuals, and people recovering from illness may need higher amounts.
Nukleotidy Supplements — Do You Need Them?
When Supplementation Is Considered
Supplements may help:
-
Athletes with high energy demands
-
People with digestive issues
-
Post‑surgery or illness recovery
-
Weak immune systems
Natural vs Synthetic Nucleotide Supplements
Natural sources are preferred, but synthetic supplements are used in medical nutrition and infant formula. Research supports their benefits in specific cases.
Dosage and Safety Considerations
Too much intake may cause imbalance. Pregnant women, kidney patients, and people with gout should consult doctors before supplementation.
Medical Importance and Applications of Nukleotidy
In Genetic Research and Gene Editing
Nukleotidy are essential in CRISPR technology, DNA sequencing, PCR testing, and genetic diagnostics.
Role in Treating Viral Infections
Some antiviral medicines mimic nucleotides to stop viruses like HIV and hepatitis from reproducing.
Cancer Research and Chemotherapy Agents
Certain drugs block nucleotide production in cancer cells, stopping tumor growth.
Nukleotidy and Gut Health
Role in Gut Lining and Repair
They help maintain the intestinal lining and support healthy digestion and nutrient absorption.
Infant Nutrition
Infant formulas often include nucleotides to support immune development and gut health in babies.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Common Side Effects
Excess intake may cause bloating, gas, or digestive discomfort.
Medical Conditions to Monitor
People with gout or kidney disease should be cautious due to uric acid production.
H3: Drug Interactions
Nukleotidy may interact with chemotherapy drugs, immunosuppressants, and blood pressure medications.
How to Incorporate Nukleotidy into Your Diet
Balanced Diet Recommendations
Eat a mix of animal and plant foods daily. Traditional meals like lentil soup, sardines, liver dishes, and whole grains are excellent sources.
Tips for Athletes and Recovering Patients
Consume nucleotide‑rich foods with protein and gut‑friendly meals to improve absorption and recovery.
Modern Research and Future Potential of Nukleotidy
Synthetic Biology and Data Storage
Scientists are using DNA nucleotides for data storage and artificial life research.
Next-Generation Therapies
Future treatments include cancer vaccines, immune therapies, and personalized genetic medicine.
Conclusion
Nukleotidy are small molecules with massive importance. They power energy, store genetic information, strengthen immunity, and support recovery and growth. Including nucleotide‑rich foods in your diet supports long‑term health, performance, and cellular strength.
FAQs About Nukleotidy
1. What are nukleotidy?
Nukleotidy (nucleotides) are small organic molecules that form DNA, RNA, and ATP. They are essential for genetic coding, energy, and cell function.
2. What is the role of nukleotidy in DNA and RNA?
Nukleotidy build DNA and RNA by linking together in specific sequences. These sequences store genetic information and guide protein creation.
3. Why are nukleotidy important for energy production?
Nukleotidy produce ATP, the cell’s energy currency. ATP powers everything from muscle movement to digestion and brain activity.
4. Which foods are rich in nukleotidy?
Nukleotidy are found in liver, seafood, poultry, legumes, mushrooms, soy, eggs, and whole grains—especially organ meats and fermented foods.
5. Do nukleotidy help the immune system?
Yes, nukleotidy support immune cell function, speed up tissue repair, and strengthen the body’s ability to fight infections.
6. Are nukleotidy supplements safe to take?
They are generally safe in moderation, but people with kidney issues, gout, or pregnant women should consult a doctor before use.